Last Updated on May 5, 2024 by Nyayik Vigyan
Facial reconstruction in forensics is also called Forensic facial reconstruction or Forensic facial approximation or Cranio-Facial reconstruction, a subtype in Forensic anthropology. It is a scientific art-based technique used in identification through human cranial remains got from crime scenes. This method has proven to be effective where other identification techniques have failed. Though the human skull appears to be like every individual, there are minor differences that make us unique.
There is a huge history that dates back to the Neolithic age but a German anatomist Wilhelm His Sr. performed the very first scientific facial reconstruction in 1895, who reconstructed three-dimensionally the face of German composer Johann Sebastian Bach (1685-1750) from his remains. He collected the data of tissue depth by inserting a thin sharp needle, having a soft rubber at its tip to minimize tissue damage. Next, the penetration depth was calculated; measurements from different anthropometric marks of the face were taken. Further, this technique was changed by Wilton Maria Krogmann in 1956. He introduced five basic relational principles to reconstruct the facial soft tissues-relation of the eyeball to orbit, ear location, and ear length, the width of the mouth, and the shape of the nose tip. Enhancements of different techniques made it more reliable, workable, and accurate.
Techniques in Facial Reconstruction:
2-D Reconstruction: Rebuilding facial appearance approx to when the person was alive, two-dimensionally using antemortem photographs and skull got.
The technique was introduced by Karen.T.Taylor in the 1980s. The remains collected, mainly the skull is taken glued with important tissue depth markers at various necessary anthropometric landmarks. Then the skull is photographed. Next, it places a transparent sheet onto the photograph of the skull in order to make a clear sketch of that individual based upon the markers. A professional artist or forensic artist in collaboration with a forensic anthropologist is required.
Photos from different angles and views such as lateral or frontal are taken. Computerized advancements like F.A.C.E (Forensic Anthropology Computer Enhancement System) and C.A.R.E.S (Computer Assisted Recovery Enhancement System) are software programs that aid in developing 2D images precisely with reduced manpower and boosting of the process.

Facial Reconstruction – 1
3-D Reconstruction: Higher developments lead to remodeling the facial structure manually. This approach involves manually creating the appearance from the facial data collected from that particular individual. We can do this method either by making sculptures or by using computer software to regenerate the appearance.
3-D sculpting method: In these casts are made of clay/wax/plasticine. First, it did a clear examination of the skull to know the symmetry of facial structures and biological features. Second, the skull replica is obtained and sculpture is made according to the data collected. Various pioneers have developed various techniques in 3-D clay sculpting such as; Russian anatomical Method, the American anthropometric method, and Manchester Method.
Russian Method: Developed by Russian anthropologist Michael Gerasimov in the 1930s. He was the first to attempt paleo-anthropological facial reconstruction to estimate the facial features of ancient people. In his method, he focused on facial muscles, glands, and cartilage. Later a layer of skin was added to complete the look.
Methods
American Method: This process is based on the Krogmann principles and the method involves modeling the skull using tissue depth markers and adding the clay or wax according to the thickness. Artificial eyeballs are fixed into the socket of the skull replica. Forgiving it complete 3D appearance, painting the eyebrows, lips, cheeks, adding hair, and other accessories are done. This gives a more realistic view of the facial features.
Manchester Method: Also known as a combined method or British method where both Russian and American methods are applied to get fine sculpture with every minute detail on it. Facial features such as eyes, nose, are calculated scientifically from the obtained skull and added onto the replica. It added even the subcutaneous fat layer made of clay to get the exact look. Researchers claim this to be the best method among all the three.
Though these methods are useful for identification, they are controversial because the involvement of artists requires highly trained professionals. Since it has manually done, there might be chances of errors, and also time-consuming. Precautions should be strictly followed because any minute distortions in the skull or during the procedure will decrease the validity.
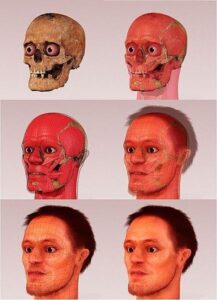
Facial Reconstruction – 2
3-D Computer-Based Method: The involvement of computers makes the task easier. Here various computer software is used to create the 3D animated image directly or by taking the help of manually created sculptures. It created the face onto a digital skull created by CT scans followed by its filling. Different databases in the software are available to recreate the face color, eye, nose, contours, etc. The last image is more convincing and practical. Superimposition is another technique which is commingled with computer-assisted reconstruction for identification purpose.
Significance of Facial Reconstruction in Criminal Investigations:
- A reliable method for the identification of unknown remains found in various crime scenes like mass murders, mass disasters, or where the body has been totally disfigured.
- Helpful for government officials in criminal profiling.
- Other biological features apart from facial appearance such as age, sex and ethnicity can be determined.
- When an unidentified body found by the police officers, they often try to find out its identity in such cases this technique can help the deceased victim’s beloved ones to identify the body and perform the last rites.
Limitations: Even the tool is helpful for identification, it has got its own drawbacks:
- We need experts to perform perfectly, which is rare.
- There is a shortage of tissue thickness data got from the analysis.
- A lot of subjectivity.
- Lack of data about facial features in case if ante-mortem photos are not available or the skull has totally deformed.
Ultimately, Facial Reconstruction is very helpful in gathering information about the unidentified dead bodies, supportive for police or investigative officers in solving crimes, and the jurors to come to a conclusive statement when the final analysis report presented as collaborative evidence in the court of law. With everyday advancements in this field like computer-assisted reconstruction despite having drawbacks, still, the experts try to experiment with it because the accuracy rate is also simultaneously better.
References
- Sonia Gupta, Vineeta Gupta, Hitesh Vij, Ruchika Vij, and Nutan Tyagi. Forensic Facial Reconstruction: The Final Frontier, 2015 Sep; 9(9): ZE26-ZE28.
- Omstead J. Facial Reconstruction. Uni West Ont Anthrol.2011;10(1):37-46
- Arpita S, et al. 3d Forensic Facial Reconstruction: A Review of the traditional sculpting Methods and Recent Computerised Developments. Int J Forensic Sci 2018, 3(1):000134.
- Images courtesy
(https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Forensic_facial_reconstruction) - https://www.crimemuseum.org/crime-library/forensic-investigation/facial-reconstruction/
- https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Forensic_facial_reconstruction
- https://kttfacialimages.com/master-2-d-facial-reconstruction/
- https://www.slideshare.net/drbhargava5745/forensic-facial-reconstruction-54301059
















Leave a Reply