Last Updated on September 29, 2023 by Nyayik Vigyan

The scientific study of structure and diseases of teeth is defined as Odontology, but when it is presented in the interest of justice it is known as Forensic Odontology.
Forensic Odontology was done mainly to reconstruct the deceased person’s age, sex, the ethnicity of the person, using dental tissues. It plays a major role in some cases such as Murder, Rapes and Juvenile delinquency, Mass disasters, Kidnappings.
Forensic Odontology is performed by Forensic Odontologists and uses the skills of a dentist to establish the identity of the person whose remains have been found.
Significance:
Teeth are the most rigid and robust tissues of the human body and it is resistant to decomposition. The teeth patterns of every individual are unique. No two individual teeth patterns are alike. Forensic Odontology helps in solving civil and criminal cases. Dental tissues are often used to determine age, race, sex of the person who can either be a victim or suspect. Like fingerprints, teeth also provide identification of deceased after analyzing ante-mortem report. Forensic Odontology can be classified in categories:
- Identification of bite marks.
- Identifying the living deceased, the skeletal remains, where dental clues are leftover.
- Age estimation on the basis of dental data.
Unidentified cadavers and human body part remain have always created a problem and blockage in the proceedings of a case
It is also for living individuals who do not have valid proof of date of birth with them
4. Sex determination
Aids in identification of the unknown individuals in natural disasters; chemical and nuclear bomb explosion scenarios
Bite Marks Analysis:
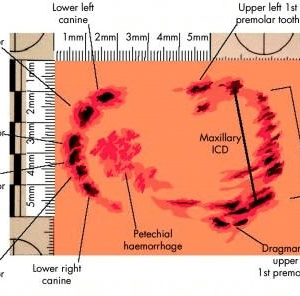
- Hemorrhage (small bleeding spot)
- Abrasion (undamming mark on the skin)
- Contusion (ruptured blood vessel)
- Laceration (near puncture of skin)
- Incision (torn skin)
- Avulsion (removal of skin)
- Artefact (bitten-off piece of body)
Palatal Rugae Analysis:

Palatal Rugae, a series of transverse ridges on the anterior part of palatal mucosa. In some situations, if teeth are lost due to any reason, the use of palatal rugae has been suggested for identification. In the study of palatal rugae, in order to identify a person’s identity, it is known as Rugoscopy/palatoscopy. Rugae are protected from trauma by their international position in the heat by tongue and buccal pad of fat. Once they formed, they do not undergo any change except in length & remain in the same position throughout the person’s lifetime.
Type of Evidence Encountered:
Evidence can be classified into 2 categories:
1. Physical Evidence
(a) Dental records
(b) Photographs
(c) Radiographs
(d) Casts
(e) Denture
2. Biological Evidence
(a) Bitemarks
(b) Palatal Rugae
(c) Tooth
(d) Saliva
(e) Lip Prints
(f) Tissue sections
Case Investigation in Which Forensic Odontology Played A Key Role:
Assault Case:
As we all are aware of the 16th December 2012, gang rape-murder of NIRBAYA which occurred in Delhi. The Forensic Dentist from SDM College from Karnataka was able to link two of the accused to the crime. They have arranged the teeth patterns along with the bite marks.
Mass Disaster Accidents:
On 28th November 1987, A Boeing 747-224B combi of SAA, the “Helderberg Crash into sea near Mauritius. All passengers on board died. The forensic dentist examined the dental tissues of 8 victims, out of 15. Out of 8 remains recorded, only 5 were identified by means of simple dental restorations, advanced dentistry, anatomical features of teeth, and stages of development of teeth. Among 5 remains, one of the victims was identified by process of exclusion and radiography.
Mass Tsunami Disaster:
On 26th December 2004, an earthquake measuring 9 on Richter scale occurred. The victim in the incident was successfully identified by forensic odontology. Forensic dentistry was divided into 2 parts.
- Dental Examination
- Dental Radiology
During the examination, the teeth received from the crime scene were identified for further radiography. Once radiographs were checked and approved, two teeth were extracted for DNA analysis. In this way, forensic odontologists helped to identify the Tsunami victims through their dental patterns .92% non-Thai were identified of which out of 80% were successfully identified by forensic odontology.
Advancing Fronts in Forensic Odontology:
- Cone beamed computed tomography.
- Digital radiography.
- DNA profiling.
- Portable Dental X-ray generator.
- Scanning electron microscopy with energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy & X-ray fluorescence.
- Computer-assisted dental identification software.
References
- www.forensicmed.co.uk
- ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pcm/articles/pmc6080160
- researchgate.net/publication/31386140







