Analysis of hair in forensic toxicology is a method used to detect the presence of drugs or other toxic substances in a person’s hair. It can provide valuable information about a person’s drug use or exposure to toxins over a period of time, which can be useful in criminal investigations or other forensic applications.
Hair analysis is based on the principle that drugs and other substances can be absorbed into the hair shaft and can be detected through laboratory testing. The concentration of the substance in the hair can be used to estimate the amount of the substance that the person was exposed to over time.

Source: science.org
Hair analysis has several advantages over other methods of drug testing, such as urine or blood analysis. Hair grows at a constant rate, so the location of a substance in the hair shaft can provide information about when the substance was used or ingested. Hair analysis can also detect drugs that may not be detectable in urine or blood after a few days or weeks.
Hair is the commonly found evidence on the crime scene related to assault cases or cases where some sort of struggle happened at the crime scenes. Matching and identification of hair serve a major role in forensic biology and serology. But also, hair serves great importance in forensic toxicology [1,2]. It is an ideal matrix for the identification of drugs and chronic poisoning. Along with the routine analysis of other visceral organs in forensic toxicological analysis, hair must also consider. It has several advantages over other biological matrices [2].
Advantages of Hair as a Matrix:
- The drug can be detected up to 90 days
- Indefinite stability
- Metabolites can also be detected
- A hair sample is quick and easy for a live subject
- Noninvasive techniques can be employed for the sample collection
- No need for preservatives to preserve the sample for further analysis.
- Segmental analysis of hair helps to study the exposure level.
- Manipulation of the result is not easy
Disadvantages of Hair as a Matrix:
- The amount of drug present is very less detected by only some of the instrumental techniques
- Medical history of the patient is required
- Require more precautions to handle the hair sample
Toxicological analysis of hair involves four major steps [3,4]:
- Collection and preparation of hair sample
- Decontamination of the hair sample
- Extraction of drug from hair
- Analysis of the extract using the analytical technique
Collection, Preparation of Hair Sample
For the analysis of drugs, head hair is preferably collected from near the scalp of the posterior vertex region of the head due to uniformity in the growth of hair [3-5]. Around 10-80mg of hair is required for the analysis depending on the method and techniques used. The growth of hair is approximately 1cm/month; thus, the segmental analysis of hair plays an important role to find out the exposure level of a drug (the condition is a medical history of the patient should be known).

The sample should be collected by trained individuals only without external contamination. Hair samples need not be required to preserve in some preservatives or refrigeration. A hair sample can simply keep in a paper envelope or wrap in aluminum foil at room temperature, in a dry place [3,5]. During the collection of samples ethical, legal, and human rights of the person should be respected [5].
After the collection aim is the extraction of drugs from the hair, it takes lots of time in the extraction and high precision to extract the complete drug without the loss of analyte.
Decontamination Procedure for Hair
The decontamination procedure of hair is done to find out the external contamination in hair it includes dust, oil, sweat, hair care products, lipids, and loosely bound drugs from the environment, which may interfere with the final result and may produce a false-positive result. The decontamination of hair is done by using organic solvents two to three times. The first wash of hair should be kept for analysis [3-5].
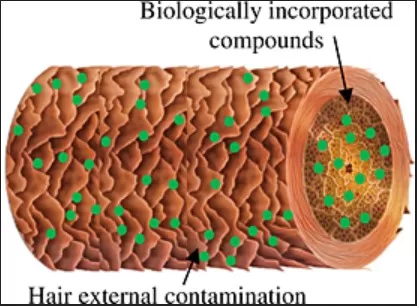 Source:analyticalsciencejournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source:analyticalsciencejournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
After decontamination hair strands should be air-dried and then segmented as fine as possible and grind into a fine powder, this fine powder is subject to extract the drug.
Extraction Procedure for Hair
The extraction of drugs requires high precision accuracy because the amount of drug present in hair is at picogram and nanogram levels [3-5]. There are three methods to extract the drug from hair.
- Acidic extraction
- Basic extraction
- Enzymatic extraction
For the extraction of the desirable analyte (acidic/basic drug), the hair sample is kept overnight in solution (acidic/basic or solution). Followed by extraction procedures such as solid-phase microextraction (SPE/SPME), and liquid-liquid extraction (LLE). In enzymatic extraction, digestion of the matrix is done by using the enzyme-like β-glucuronidase/arylsulfatase which results in the extraction of drugs from the hair [5]. The extracts thus collected is subject to analysis using various analytical technique.
Steps involved in the analysis of hair in forensic toxicology
There are several steps involved in the analysis of hair in forensic toxicology. First, a sample of hair is collected from the person being tested. This can be done by cutting a small section of hair close to the scalp or plucking individual hairs from different areas of the head. The sample should be collected in a clean and secure manner to ensure the integrity of the sample and prevent contamination.
Next, the hair sample is prepared for analysis. This may involve cutting the hair into small sections, extracting any drugs or toxins from the hair, and preparing the sample for testing using specialized laboratory equipment.
Finally, the sample is analyzed using a variety of techniques, such as chromatography or mass spectrometry, to detect the presence of drugs or other substances. The results of the analysis are then interpreted and reported to the requesting party, such as a law enforcement agency or a court of law.
Hair analysis is just one tool that can be used in forensic toxicology, and it is often used in conjunction with other methods, such as urine or blood analysis, to provide a more complete picture of a person’s drug use or exposure to toxins. It is important to note that the results of hair analysis should be interpreted with caution and should be considered in the context of other available information about the person being tested.
Analysis of Analytes Extracted from Hair
The final step for drug identification from hair is the analysis. The analysis of analyte extracted from hair requires very sophisticated and sensitive techniques because the analyte present in hair is in a very little small amount. In the last few years, many researches have been done to analyze the drug at the nanogram and picogram level. Gas chromatography-electron ionization/ mass spectrometry (GC-EI/MS), Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), LC-MS, Ultrahigh-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry (UHPLC-MS/MS) are the some analytical analyze used to detect an analyte in such small quantity [6-9].
Also, the quantification of drugs present in hair is also possible by applying these techniques.
Purpose of analysis of hair in forensic toxicology
The purpose of analysis of hair in forensic toxicology is to detect the presence of drugs or other toxic substances in a person’s hair, which can provide valuable information about a person’s drug use or exposure to toxins over a period of time. This information can be useful in criminal investigations or other forensic applications.
Techniques used in the analysis of hair in forensic toxicology
Analysis of hair in forensic toxicology is typically analyzed using techniques such as chromatography or mass spectrometry, which can detect the presence of drugs or other substances in the hair. The results of the analysis are then interpreted and reported to the requesting party.
In hair how long can drugs or other substances be detected through analysis of hair in forensic toxicology?
The length of time that drugs or other substances can be detected in hair through analysis of hair in forensic toxicology depends on a number of factors, such as the type of substance, the frequency of use, and the rate of hair growth. In general, drugs and other substances can be detected in hair for longer periods of time than they can be detected in urine or blood. For example, drugs may be detectable in hair for several months after use, while they may only be detectable in urine or blood for a few days or weeks.
The results of the analysis of hair in forensic toxicology are challenged in court
The results of the analysis of hair in forensic toxicology, like any other form of scientific evidence, can be challenged in court. The admissibility of hair analysis as evidence in court may depend on the specific laws and rules of evidence that apply in the jurisdiction where the case is being tried. In some cases, the defense may challenge the accuracy or reliability of the hair analysis or the qualifications of the person who conducted the analysis.
Analysis of hair in forensic toxicology be used to determine the cause of death
Analysis of hair in forensic toxicology can provide information about a person’s drug use or exposure to toxins, but it is not typically used to determine the cause of death. The cause of death is usually determined through a combination of factors, including the results of an autopsy, toxicology testing, and other medical and forensic examinations. Hair analysis may be used as part of this process to help provide additional information about the person’s health and drug use, but it is not typically used as the sole basis for determining the cause of death.
Analysis of hair in forensic toxicology be used to test for alcohol use
Yes, analysis of hair in forensic toxicology can be used to test for alcohol use. Alcohol is metabolized by the body and can be detected in hair through analysis. However, the sensitivity of hair analysis for detecting alcohol use is lower than for other substances, such as drugs, and it may not be as reliable as other methods, such as breath or blood testing, for detecting recent alcohol use. Hair analysis may be more useful for detecting long-term alcohol use or for determining the pattern of alcohol use over time.
Analysis of hair in forensic toxicology be used to test for illegal drugs
Yes, analysis of hair in forensic toxicology can be used to test for illegal drugs, such as cocaine, marijuana, and methamphetamine. The presence of these drugs in hair can be detected through laboratory testing and can provide valuable information about a person’s drug use or exposure to drugs.
Analysis of hair in forensic toxicology be used to test for prescription drugs
Yes, analysis of hair in forensic toxicology can be used to test for prescription drugs, such as opioids, sedatives, and stimulants. The presence of these drugs in hair can be detected through laboratory testing and can provide valuable information about a person’s drug use or exposure to drugs.
Analysis of hair in forensic toxicology be used to test for environmental toxins
Yes, analysis of hair in forensic toxicology can be used to test for environmental toxins, such as heavy metals, pesticides, and industrial chemicals. The presence of these toxins in hair can be detected through laboratory testing and can provide valuable information about a person’s exposure to toxins.
Analysis of hair in forensic toxicology be used to test for alcohol or drug use during pregnancy
Yes, analysis of hair in forensic toxicology can be used to test for alcohol or drug use during pregnancy. The presence of alcohol or drugs in the hair of a pregnant woman can be detected through laboratory testing and can provide valuable information about the woman’s alcohol or drug use during pregnancy. This information can be used to assess the potential impact of alcohol or drug use on the health of the unborn child and to provide appropriate care and support to the mother and child.
Analysis of hair in forensic toxicology be used to test for the use of over-the-counter drugs
Yes, analysis of hair in forensic toxicology can be used to test for the use of over-the-counter drugs, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and acetaminophen. The presence of these drugs in hair can be detected through laboratory testing and can provide valuable information about a person’s use of over-the-counter drugs. This information can be used in cases where the use of over-the-counter drugs may be relevant, such as in workplace drug testing or in cases of overdose or poisoning.
Analysis of hair in forensic toxicology be used to test for the use of herbal or alternative remedies
Yes, analysis of hair in forensic toxicology can be used to test for the use of herbal or alternative remedies. Some herbs and other natural substances can contain active ingredients that can be detected through laboratory testing. However, the detection of these substances in hair may be more challenging than the detection of synthetic drugs, as the compounds found in herbs and other natural substances may be more complex and may vary in their chemical makeup. It is important to note that the ability to detect the use of herbal or alternative remedies through hair analysis may depend on the specific laboratory techniques and methods used and the availability of reference standards for the substances being tested.
Limitation of analysis of hair in forensic toxicology
However, the analysis of hair in forensic toxicology also has some limitations. The accuracy of the test can be affected by the type of substance being tested for, the length and condition of the hair, and the method of analysis used. In addition, hair analysis is more expensive and time-consuming than other methods of drug testing, and it may not be suitable for all types of substances or situations.
Analysis of hair in forensic toxicology has other limitations it is important to interpret the results of hair analysis with caution and to consider them in the context of other available information about the person being tested.
Conclusion
In the field of forensic toxicology, hair as a matrix should also consider along with the other biological matrix and visceral samples. It has several advantages over other biological matrices. There are some factors that affect the analysis, these factors should also consider during hair analysis such as external decontamination, hair care product use, hair color, cosmetic treatments, and the concentration of dose. There are several studies on hair analysis and methods have been developed, but still, there is a need for more research and study in the same field.
References
- T. Oien, C. A. R. R. Y. (2009, April). Forensic Hair Comparison: Background Information for Interpretation. Forensic Science Communications. https://archives.fbi.gov/archives/about-us/lab/forensic-science-communications/fsc/april2009/review/2009_04_review02.htm
- Usman, Muhammad & Naseer, Abid & Baig, Yawar & Jamshaid, Tahir & Shahwar, Muhammad & Khurshid, Shazia. (2019). Forensic toxicological analysis of hair: a review. Egyptian Journal of Forensic Sciences. 9. 17. 10.1186/s41935-019-0119-5.
- Society of Hair Testing (2004). Recommendations for hair testing in forensic cases. Forensic science international, 145(2-3), 83–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2004.04.022
- Cooper, G.A. &Kronstrand, R. &Kintz, P. & T, Society. (2012). Society of hair testing guidelines for drug testing in hair. Forensic Sci. Int. 20.
- Khajuria, H., Nayak, B. P., & Badiye, A. (2018). Toxicological hair analysis: Pre-analytical, analytical and interpretive aspects. Medicine, Science and the Law, 58(3), 137-146. doi:10.1177/0025802418768305
- Kronstrand, R., Forsman, M., & Roman, M. (2013). A screening method for 30 drugs in hair using ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Therapeutic drug monitoring, 35(3), 288–295.
- Khajuria, H., Nayak, B. P., & Badiye, A. (2018). Toxicological hair analysis: Pre-analytical, analytical and interpretive aspects. Medicine, science, and the law, 58(3), 137–146. https://doi.org/10.1177/0025802418768305
- Cuypers, E., & Flanagan, R. J. (2018). The interpretation of hair analysis for drugs and drug metabolites. Clinical toxicology (Philadelphia, Pa.), 56(2), 90–100. https://doi.org/10.1080/15563650.2017.1379603
- Di Corcia, D., Salomone, A., & Gerace, E. (2018). Analysis of Drugs of Abuse in Hair Samples by Ultrahigh-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry (UHPLC-MS/MS). Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N.J.), 1810, 107–114. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-8579-1_10

